About Nisin
Nisin, the active ingredient in Niseen®, is a polycyclic antibacterial peptide with 34 amino acid residues used to prevent spoilage and extend shelf life of various foods by inhibiting Gram-positive spoilage and pathogens. Nisin is effective against a wide range of Gram-positive bacteria, both as vegetative cells and as spores, used worldwide since 1953 to control bacterial spoilage in both heatprocessed and low-pH foods. It is a small peptide produced by Lactococcus lactis, a bacterium which occurs naturally in milk.
History
Nisin was found naturally in milk in 1950s, and commercialized at 2.5% concentration in 1953. In 1969, Nisin was approved for use as an antimicrobial in
food by the Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives. After then Nisin has been given E number E234 in Europe as natural food additives and is permitted currently for use in over 50 countries.
Chemical specification
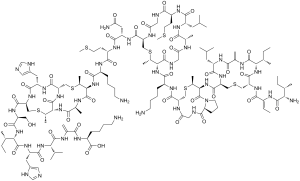
CAS number: 1414-45-5
E number: E 234
Molecular formula: C143H230N42O37S7
Molar mass: 3354.07 g/mol
Boiling point: 2966 °C, 3239 K, 5371 °F
Density: 1.402 g/mL
Function
Nisin works in a concentration dependent fashion; thus the more bacteria present in a food the more Nisin may be required. Nisin initially forms a complex with Lipid II, a precursor molecule in the formation of bacterial cell walls. The Nisin–lipid II complex then inserts itself into the cytoplasmic membrane forming pores and allows the efflux of essential cellular components resulting in inhibition or death of the bacteria.
Safety
Nisin is a natural antibacterial food preservative as it is a polypeptide produced by certain strains of the food-grade lactic acid bacterium Lactococcus lactis subsp. lactis during fermentation production. Research also shows it is also toxicologically safe. In 1969, Nisin was approved for use as an antimicrobial in food by the Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives.

